Introduction
Strict
interpretation of geometric construction allows use of only the compass and an
instrument for drawing straight lines, and with these, the geometer, following
mathematical theory, accomplishes his solutions. In technical drawing, the principles
of geometry are employed constantly, but instruments are not limited to the
basic two as T-squares, triangles, scales, curves etc. are used to make
constructions with speed and accuracy. Since there is continual application of
geometric principles, the methods given in this topic should be mastered
thoroughly. It is assumed that students using this book understand the elements
of plane geometry and will be able to apply their knowledge.
The
constructions given here afford excellent practice in the use of instruments.
Remember that the results you obtain will be only as accurate as your skill
makes them. Take care in measuring and drawing so that your drawings will be
accurate and professional in appearance.
A. Points In Space
A point
is an exact location in space or on a drawing surface.
A point
is actually represented on the drawing by a crisscross at its exact location.
The exact point in space is where the two lines of the crisscross intersect.
When a point is located on an existing line, a light, short dashed line or
cross bar is placed on the line at the location of the exact point. Never
represent a point on a drawing by a dot; except for sketching locations.
B. Line
Lines
are straight elements that have no width, but are infinite in length
(magnitude), and they can be located by two points which are not on the same
spot but fall along the line. Lines may be straight lines or curved lines. A
straight line is the shortest distance between two points. It can be drawn in
any direction. If a line is indefinite, and the ends are not fixed in length,
the actual length is a matter of convenience. If the end points of a line are
important, they must be marked by means of small, mechanically drawn crossbars,
as described by a pint in space.
Straight
lines and curved lines are considered parallel if the shortest distance between
them remains constant. The symbol used for parallel line is //. Lines, which
are tangent and at 90⁰ are considered perpendicular. The symbol for perpendicular line is ⊥.
C. Angle
An
angle is formed by the intersection of two lines. There are three major kinds
of angles: right angels, acute angles and
obtuse
angles. The right angle is an angle of 90⁰, an acute
Angle
is an angle less than 900, and an obtuse angle is
an
Angle
more than 90⁰, A straight line is 180⁰. The symbol for an angle is < (singular) and
<’s (Plural). To draw an angle, use the drafting machine, a triangle, or a
protractor.
D. Triangles
A
triangle is a closed plane figure with three straight sides and their interior
angles sum up exactly 1800. The various kinds of triangles:
a right triangle, an equilateral triangle, an isosceles triangle, and an obtuse
angled triangle.
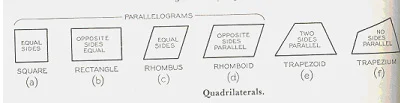
E. Quadrialteral
It is a
plane figure bounded by four straight sides. When opposite sides are parallel,
the quadrilateral is also considered to be a parallelogram.
F. Polygon
A
polygon is a closed plane figure with three or more straight sides. The most
important of these polygons as they relate to drafting are probably the
triangle with three sides, square with four sides, the hexagon with six sides,
and the octagon with eight sides.
G. Circle
A
circle is a closed curve with all points on the circle at the same distance
from the center point. The major components of a circle are the diameter, the
radius and circumference.
- The
diameter of the circle is the straight distance
from one outside curved surface through the center point to the opposite
outside curved surface.
- The
radius of a circle is the distance from the center point to the
outside curved surface. The radius is half the diameter, and is used to set the
compass when drawing a diameter.
- A
central angle: is an angle formed by two radial lines from the
center of the circle.
- A
sector: is the area of a circle lying between two
radial lines and the circumference.
- A
quadrant: is a sector with a central angle of 900 and usually with one of the radial lines oriented
horizontally.
- A
chord: is any straight line whose opposite ends terminate
on the circumference of the circle.
- A
segment: is the smaller portion of a circle separated by
a chord.
- Concentric
circles are two or more circles with a common center
point.
- Eccentric
circles are two or more circles without a common center
point.
- A semi circle is half of the circle.
H. Solids
They
are geometric figures bounded by plane surfaces. The surfaces are called faces, and if these are equal regular polygons, the solids are regular polyhedra.
- Techniques Of
Geometric Constructions
To
construct the above mentioned geometric figures, we have to know some
principles and procedures of geometric construction. Thus, the remaining of
this chapter is devoted to illustrate step-by-step geometric construction
procedures used by drafters and technicians to develop various geometric forms.
A. How To Bisect A Line Or An Arc
To
bisect a line means to divide it in half or to find its center point. In the
given process, a line will also be constructed at the exact center point at
exactly 90⁰.
Given: Line A-B.
Step 1:
Set the compass approximately two-thirds of the length of line A-B and swing an
arc from point A.
Step 2:
Using the exact same compass setting, swing an arc from point B.
Step 3:
At the two intersections of these arcs, locate points D and E.
Step 4:
Draw a straight-line connecting point D with point E.
Where
this line intersects line A-B, it bisects line A-B.
Line
D-E is also perpendicular to line A-B at the exact center point.
B. How To Divide A
Line In To Number Of Equal Parts
Given: Line A-B.
Step 1:
Draw a construction line AC that starts at end A of given line AB. This new
line is longer than the given line and makes an angle of not more than 300 with it.
Step 2:
Find a scale that will approximately divide the line AB in to the number of
parts needed (11 in the example below), and mark these divisions on the line
AC.
There
are now ‘n’ equal divisions from A to D that lie on the line AC (11 in this example).
Step 3:
Set the adjustable triangle to draw a construction line from point D to point
B. Then draw construction lines through each of the remaining ‘n-1’ divisions
parallel to the first line BD by sliding the triangle along the straight edge. The original line AB will now be accurately divided.
C. How To Bisect An
Angle
To
bisect an angle means to divide it in half or to cut it in to two equal angles.
Given: Angle BAC.
Step 1:
Set the compass at any convenient radius and swing an arc from point A.
Step 2:
Locate points E and F on the legs of the angle, and swing two arcs of the same
identical length from points E and F, respectively.
Step 3:
Where these arcs intersect, locate point D. Draw a straight line from A to D.
This line will bisect angle BAC and establish two equal angles: CAD and BAD.
D. How To Draw An Arc Or Circle (Radius) Through Three Given Points
Given: Three points in space at random: A, Band C.
Step 1:
With straight line, lightly connect points A to B, and B to C.
Step 2:
Using the method outlined for bisecting a line, bisect lines A-B and B-C.
Step 3:
Locate point X where the two extended bisectors meet. Point X is the exact
center of the arc or circle.
Step 4:
Place the point of the compass on point X and adjust the lead to any of the
points A, B, or C (they are the same distance), and swing the circle. If all
work is done correctly, the arc or circle should pass through each point.
E. How To Draw A Line
Parallel To A Straight Line At A Given Distance
Given: Line A-B, and a required distance to the parallel line.
Step 1:
Set the compass at the required distance to the parallel line. Place the point
of the compass at any location on the given line, and swing a light arc whose radius
is the required distance.
Step 2:
Adjust the straight edge of either a drafting machine or an adjusted triangle
so that it line sup with line A-B, slide the straight edge up or down to the
extreme high point, which is the tangent point, of the arc, then draw the
parallel line.
F. How To Draw A Line
Parallel To A Line Curved Line At A Given Distance
Given: Curved line A-B, and a required distance to the parallel line,
Step 1:
Set the compass at the required distance to the parallel line. Starting from
either end of the curved line, place the point of the compass on the given
line, and swing a series of light arcs along the given line.
Step 2:
using an irregular curve, draw a line along the extreme high points of the
arcs.
G. How To Draw A Perpendicular Lines To A Line At A Point
Method 1
Given: Line A-B with point P on the same line.
Step 1:
Using P as a center, make two arcs of equal radius or more continuous arc (R1)
to intercept line A-B on either side of point P, at points S and T.
Step 2:
Swing larger but equal arcs (R2) from each of points S and T to cross each
other at point U.
Step 3:
A line from P to U is perpendicular to line A-B at point P.
H. How To Draw A Perpendicular To A Line At A Point
Method 2
Given: Line A-B with point P on the line.
Step 1:
Swing an arc of any convenient radius whose center O is at any convenient
location NOT on line A-B, but positioned to make the arc cross line A-B at
points P and Q.
Step 2:
A line from point Q through center O intercepts the opposite side of the arc at
point R.
Step 3:
Line R-P is perpendicular to line A-B (A right angle has been inscribed in a semi
circle).
I. How To Draw A Perpendicular To A Line From A Point Not On The Line
Given: Line
A-B and point P.
Step 1: Using P as a center, swing an arc (R1) to
intercept line A-B at points G and H.
Step 2:
Swing larger, but equal length arcs (R2) from each of the points G and H to
intercept each other at point J.
Step 3:
Line P-J is perpendicular to line A-B.
J. How To Draw A Triangle With Known Lengths Of Sides
Given: lengths 1, 2, and 3.
Step 1:
Draw the longest length line, in this example length 3, with ends A and B.
Swing an arc (R1) from point A whose radius is either length 1 or length 2; in
this example length 1.
Step 2;
using the radius length not used in step 1, swing an arc (R2) from point B to
intercept the arc swung from point A at point.
Step 3:
Connect A to C and B to C to complete the triangle.
K. How To Draw A Square
Method-1
Given: The locations of the center and the required distance across the sides
of a square.
Step 1:
Lightly draw a circle with a diameter equal to the distance around the sides of
the square. Set the compass at half the required diameter.
Step 2:
Using triangles, lightly complete the square by constructing tangent lines to
the circle. Allow the light construction lines to project from the square, with
out erasing them.
Step 3:
Check to see that there are four equal sides and, if so, darken in the actual
square using the correct line thickness.
Method-2
Given
one side AB. Through point A, draw a perpendicular.
With A
as a center, and AB as radius; draw the arc to intersect the perpendicular at
C. With B and C as centers, and AB as radius, strike arcs to intersect at D.
Draw line CD and BD.
L. How To Draw A
Pentagon (5 Sides)
Given: The locations of the pentagon center and the diameter that will
circumscribe the pentagon.
Step 1:
Bisect radius OD at C.
Step 2:
With C as center, and CA as radius, strike arc AE.
With A
as center, and AE as radius, strike arc EB.
Step 3:
Draw line AB, then set off distances AB around the circumference of the circle,
and draw the sides through these points.
M. How To Draw A
Hexagon (6 Sides)
N. To Draw Any Sided
Regular Polygon
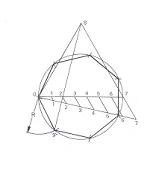
To
construct a regular polygon with a specific number of sides, divide the given
diameter using the parallel line method as shown in fig below. In this example,
let us assume seven sided regular polygon. Construct an equilateral triangle
(0-7-8) with the diameter (0-7) as one of its sides. Draw a line from the apex
(point 8) through the second point on the line (point 2). Extend line 8-2 until
it intersects the circle at point 9.
Radius
0-9 will be the size of each side of the figure. Using radius 0-9 steps off the
corners of the seven sides polygon and connect the points.
O. To Draw A Circle
Tangent To A Line At A Given Point
Given: Given line AB and a point on the line.
Step 1:
At P erect a perpendicular to the line.
Step 2:
Set off the radius of the required circle on the perpendicular.
Step 3:
Draw circle with radius CP.
P. To Draw A Tangent To A Circle Through A Point
Method-1
Given: Point P on the
circle.
Move
the T-square and triangle as a unit until one side of the triangle passes
through the point P and the center of the circle; then slide the triangle until
the other side passes through point P, and draw the required tangent.
Method-2
Given: Point P outside the circle.
Move
the T-square and triangles as a unit until one side of the triangle passes
through point P and, by inspection, is the tangent to the circle; and then slide
the triangle until the other side passes through the center of the circle, and
lightly mark the point of tangency T. finally move the triangle back to its starting
position and draw the required tangent.
Q. To Draw Tangents To Two Circles
Move
the T-square and triangles as a unit until one side of the triangle is tangent,
by inspection, to the two circles; then slide the triangle until the other side
passes through the center of one circle, and lightly mark the point of
tangency. Then slide the triangle until the side passes through the center of
the other circle, and mark the point of tangency. Finally slide the triangle
back to the tangent position, and draw the tangent lines between the two points
of tangency. Draw the second tangent line in similar manner.
R. How To Construct An Arc Tangent To An Angle
Given: A right angle, lines A and B and a required radius.
Step 1:
Set the compass at the required radius and, out of the way, swing a radius from
line A and one from line B.
Step 2:
From the extreme high points of each radius, construct a light line parallel to
line A and another line parallel to line B.
Step 3:
Where these lines intersect is the exact location of the required swing point.
Set the compass point on the swing point and lightly construct the required
radius.
Allow
the radius swing to extend past the required area. It is important to locate
all tangent points (T.P) before darkening in.
Step 4:
Check all work and darken in the radius using the correct line thickness.
Darken in connecting straight lines as required. Always construct compass work first,
followed by straight lines. Leave all light construction lines.
S. How To Construct An Arc Tangent To Two Radii Or Diameters
Given: Diameter A and arc B with center points located, and the required
radius.
Step 1:
Set the compass at the required radius and, out of the way, swing a radius of
the required length from a point on the circumference of given diameter A. Out
of the way, swing a required radius from a point on the circumference of a
given arc B.
Step 2:
From the extreme high points of each radius, construct a light radius outside of
the given radii A and B.
Step 3:
Where these arcs intersect is the exact location of the required swing point.
Set the compass point on the swing point and lightly construct the required
radius.
Allow
the radius swing to extend past the required area.
Step 4:
Check all work; darken in the radii using the correct line thickness. Darken in
the arcs or radii in consecutive order from left to right or from right to
left, thus constructing a smooth connecting line having no apparent change in
direction.
T. To Draw An Ellipse
(By Four-Centered Method)
Join 1
and 3, layoff 3-5 equal to 01-03. This is done graphically as indicated in the fig.
Below by swinging 1 around to 5 with O as center where now 03 from 05 is 3-5;
the required distance. With 3 as center, an arc from 5 to the diagonal 1-3
locates 6. Bisect 1-6 by a perpendicular crossing
0-1
at 9 and intersecting 0-4 produced (if necessary)
at 10.
Make
0-9’ equal to 0-9, and 0-10’ equal to 0-10. Then 9, 9’, 10, and 10’ will be
centers for four tangent circle arcs forming a curve approximating the shape of
an ellipse.
U. How To Draw An
Ogee Curve
An ogee
curve is used to join two parallel lines. It forms a gentle curve that reverses
itself in a neat symmetrical geometric form.
Given: Parallel lines A-B and C-D.
Step 1:
Draw a straight line connecting the space between the parallel lines. In this
example, from point B to point C.
Step 2:
Make a perpendicular bisector to line B-C to establish point X.
Step 3:
Draw a perpendicular from line A-B at point B to intersect the perpendicular
bisector of B-X, which locates the first required swing center. Draw a perpendicular
from line C-D at point C to intersect the perpendicular bisector of CX, which
locates the second required swing center.
Step 4:
Place the compass point and adjust the compass lead to point B, and swing an
arc from B to X. Place the compass point on the second swing point and swing an
arc from X to C. This completes the ogee curve.